NGC's Cygnus freighter spacecraft Fires Engine for Limited ISS Reboost
- Karthik Naren
- Jun 25, 2022
- 1 min read

On Saturday, June 25, American aerospace company: Northrop Grumman's Cargo Spacecraft “Cygnus” completed its first limited reboost of the International Space Station. Cygnus’ gimbaled delta velocity engine was used to adjust the space station’s orbit through a reboost of the altitude of the space station.
The maneuver lasted 301 seconds, which raised the station’s altitude by 160 meters at apogee and 804 meters at perigee.
This reboost follows an initial attempted reboost on June 20 which was terminated early as a conservative measure due to system parameters that differed from Cygnus flight operations. Investigation by engineers showed that these parameters were acceptable for the reboost and the limits were adjusted for Saturday’s attempt.
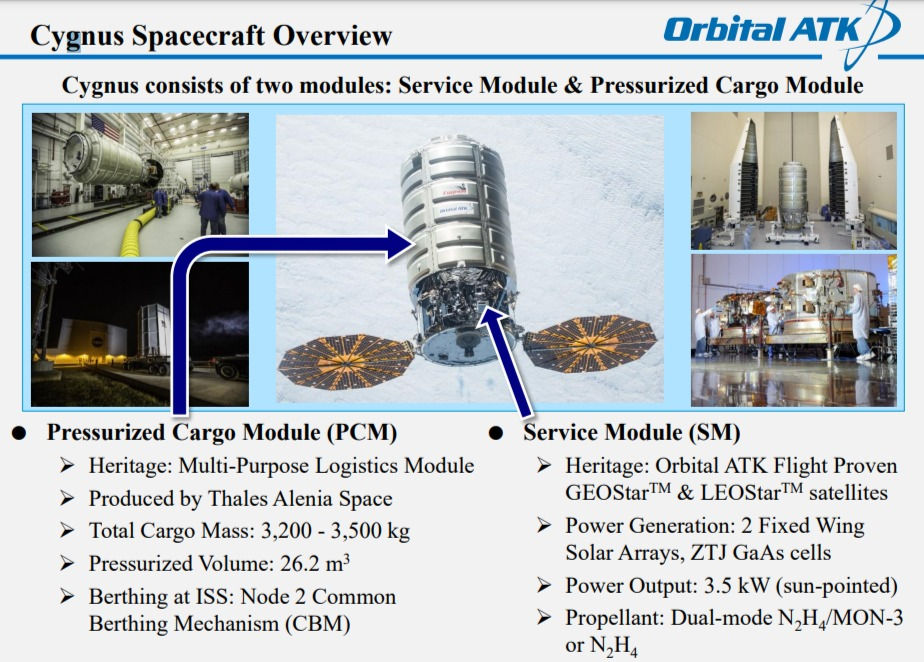
This Cygnus NG-17 mission is the first to feature this enhanced capability as a standard service for NASA, following a test of the maneuver which was performed in 2018 during Cygnus’s ninth resupply mission "CRS OA-9E". Cygnus arrived at the orbital outpost in February and is slated to depart from the space station Tuesday, June 28, where it will burn up in the Earth’s upper atmosphere.










Comments